Innate and Learned Behaviour (AHL)
Innate and Learned Behaviour (AHL): Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Operant Conditioning, Reflex Arc, Classical Conditioning, Pavlov's Classical Conditioning Theory, Animal Behaviour, Innate Behaviour, Imprinting Behaviour in Animals, Learned Behaviour and, Conditioned Stimulus
Important Questions on Innate and Learned Behaviour (AHL)
Define unconditioned stimulus with an example.
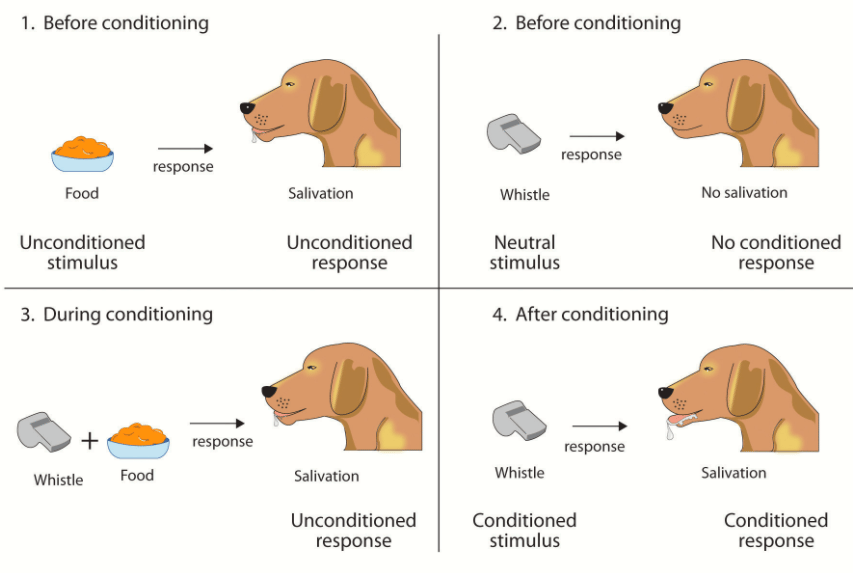
How can you say that the food is an unconditioned stimulus and the sound of the sound of bell is the conditioned stimulus
A conditioned stimulus is one that can elicit a conditioned response in the future.
Describe a conditioned stimulus.
The behaviour in animals that is occurs naturally is called learned behaviour.
Describe learned behaviour in animals.
Which among the following is not an example of innate behaviour in animals?
What do you understand by innate behaviour in animals?
Give examples of classical conditioning.
How is Classical conditioning different from the operant conditioning?
What is operant conditioning? How it is different from the Pavlov conditioning?
The human babies learn to speak by mimicking their parents. It is an example of
What do you understand by imprinting behaviour in animals?
Motor neuron is not a part of reflex arc.
Cutting up an onion makes your eyes water is an example of:
Which of the following is part of classical conditioning?
The stimulus that causes an automatic reaction is known as:
The process by which a conditioned stimulus acquires the ability to elicit a conditioned response is known as:
The conditioned stimulus is associated with:
Which of the following is/ are example(s) of innate reflex action?
